Understanding and Overcoming Depression: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Options
Introduction
Depression is a widespread mental illness that impacts millions of people around the world.
Its symptoms can include persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and despair, as well as physical symptoms like fatigue, changes in appetite or sleep patterns, and difficulty concentrating.
Depression can have various causes, including genetics, environmental factors, and life events such as trauma, loss, or stress.
It can also coexist with other mental health disorders, like anxiety or substance abuse.
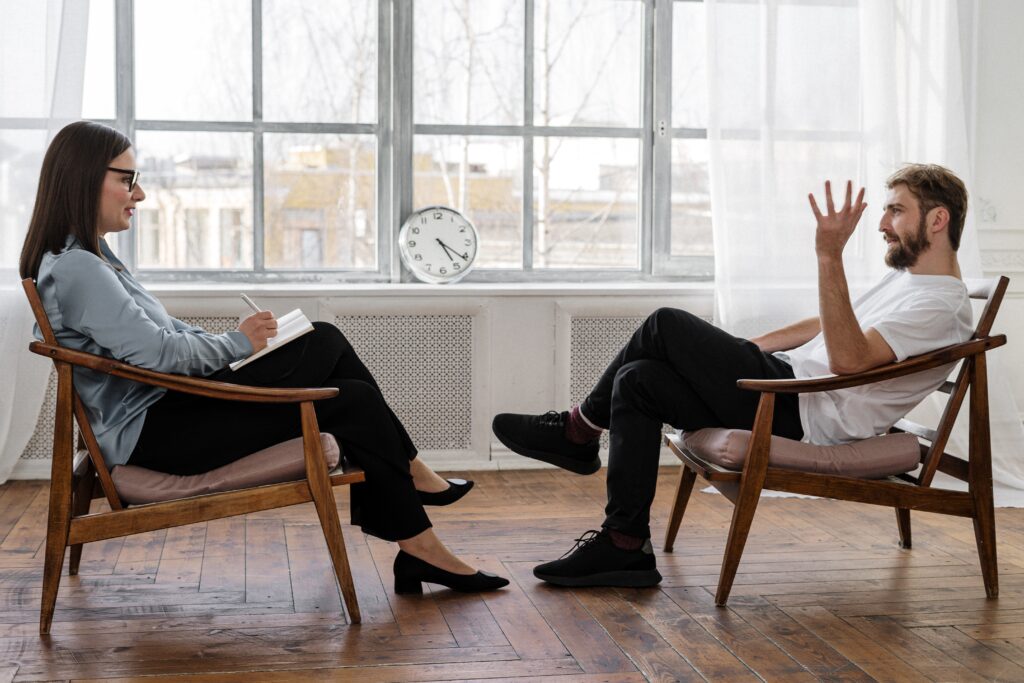
Treatment options for depression usually involve a combination of medication and therapy to reduce symptoms and improve overall well-being.
Medications like antidepressants work by altering brain chemistry to regulate mood, while therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors.
Preventing and managing depression can involve lifestyle changes like regular exercise, a healthy diet, and adequate sleep.
It is also essential to seek help from a mental health professional if symptoms persist or worsen.
Overall, depression is a complex and challenging condition that requires a comprehensive approach to treatment and management.
By understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatment options, we can work towards better outcomes for those who are affected by this illness.